Nitrogen Vacuum Reflow Soldering
Nitrogen vacuum reflow soldering is a nitrogen-protected reflow soldering technology performed in a vacuum environment. During the reflow soldering process, the components to be soldered are placed in a vacuum chamber, and high-purity nitrogen is injected into the vacuum environment. Nitrogen helps eliminate oxygen, reduce oxidation, and improve solder joint quality. Nitrogen vacuum reflow soldering is suitable for soldering various high-reliability electronic components, but it has relatively high equipment costs and operating costs.
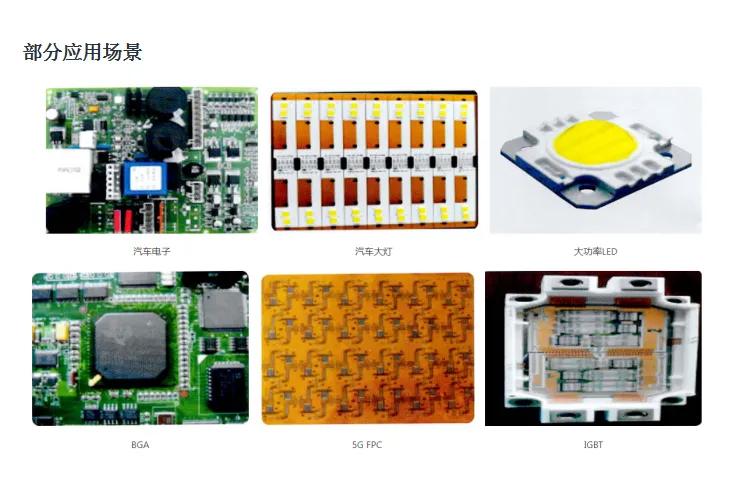
It is applicable to high-precision and ultra-high-demand fields such as semiconductors, aerospace, national defense and military industry, medical care, a utomotive electronics, 5G communications, and LEDs. It features efficient heating and precise control. Adopting a patented structure and heating technology, it can reach a heating temperature of 350°C with a temperature control accuracy of ±1°C, effectively solving the problem of suppressing void rates in the soldering of mid-to-high-end products.
- Aluminum substrates
- Copper substrates
- Rigid-flex boards
- FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) boards
- 10-layer, 20-layer, and 36-layer high-difficulty control boards
- High-complexity module boards
- BGA (Ball Grid Array), QFN (Quad Flat No-lead), AQFN (Advanced Quad Flat No-lead), IBGT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor)
- Modules and blocks
- Various high-power devices and modules in special fields such as POP (Package on Package)
- Aerospace, military industry, automotive electronics, rail transit
- Artificial intelligence, 5G communications, medical care, semiconductors
- Special lighting, digital currency, special servers
The void rate of vacuum reflow soldering can be controlled at 1%, 1.5%, or 2% (compared to approximately 20% for traditional air reflow soldering and nitrogen reflow soldering).
- Product safety and reliability
- Usage reliability
- End-product safety and reliability
- Production process reliability
- Production process stability
- Production yield reliability
Introducing Vacuum Conditions
Vacuum soldering technology is a type of reflow soldering technique that introduces a vacuum environment during the reflow soldering process. A vacuum environment is created in the latter stage when the product enters the reflow zone to improve soldering quality.
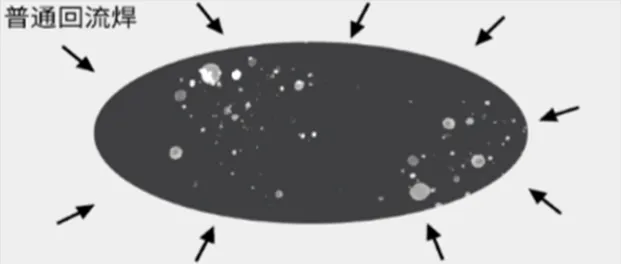
During conventional reflow soldering, air pressure hinders the escape of bubbles from the solder. These bubbles then form voids in the solder joints after cooling.
Utilizing pressure difference to expel bubbles
The external environment of solder joints in a molten state is close to a vacuum. Due to the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the solder joints, the bubbles inside the solder joints are expelled, which significantly reduces the void rate of the solder joints and improves their reliability.
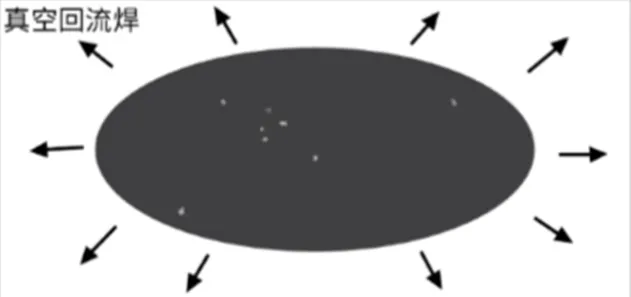
During soldering, the molten solder pool is placed in a negative-pressure vacuum. The pressure difference is used to force bubbles out, thereby reducing voids.During soldering, the molten solder pool is placed in a negative-pressure vacuum. The pressure difference is used to force bubbles out, thereby reducing voids.
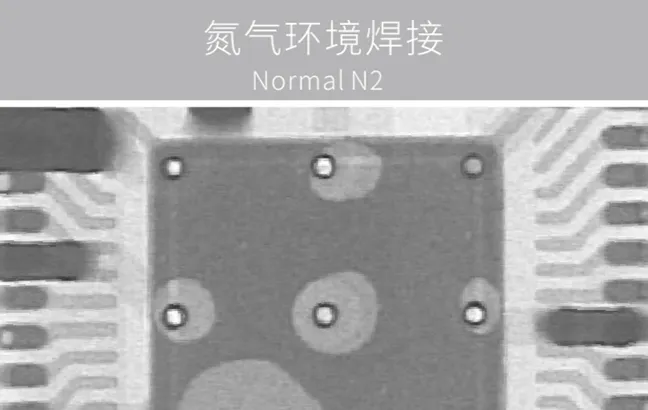
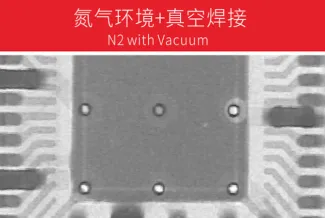
Under normal atmospheric pressure, the occurrence rate During soldering in a vacuum pressure environment,
of bubbles during soldering is approximately 25% the occurrence rate of bubbles isapproximately 1% to 5%, and can even be as low as around 0.5% in some cases.







![]()
![]()



